Full Guide: Getting a home loan in Japan for foreigners
If you are a foreigner living in or planning to live in Japan, you may be wondering if you can get a housing loan when you want to build or buy a house in Japan. The short answer is, yes - however, it is important to understand the overview of the system and the requirements for housing loans.
Below is the quick summary of housing loans in Japan for foreigners:
- All foreigners can buy land or a property and most of foreign residents can apply for housing loans in Japan.
- It is preferable to have a permanent residence if you are applying for a house loan to a Japanese financial institution.
- Some financial institutions have house loan products specifically for people without permanent residence
We would first like to introduce the overview of house loans in Japan. Later in the chapter, we will explain the eligibility and job requirements needed to apply for a house loan when you are building or buying a house in Japan.
Table of Contents
1. What is a house loan and how does it work in Japan?
A home/housing loan, also known as a mortgage, refers to the money that an individual borrows in order to purchase a property or a house. Here we first summarize the types and features of housing loans in Japan as basic knowledge. Understanding the differences between each type of house loan will enable you to apply for a home loan best suited to your needs and financial conditions.
1-1. Types of loans
There are mainly three types of housing loans in Japan:
- Public loans: provided by public institution such as a local municipality
- Private loans: provided by banks, credit unions, and loans for life insurance purchasers. Majority of the house loans are provided in this form.
- Flat 35 loan: provided by local banks and securitized by a government affiliate called Housing Finance Agency (JHF)
1-2. Types of interests rates
There are mainly three types of interest rates:
- Fixed interest rate: interest rate is first determined at the time of contract of house loans.
- Floating interest rate: interest rate that changes with the market over the duration of the house loans.
- Hybrid adjustable interest rate: combines features of a fixed and floating interest rate.
1-3. Repayment of house loans
There are mainly three types of repayment methods:
- Principal and interest equal repayment (元利均等返済):common repayment method with a fixed principal amount on a specified date of each month. The total amount you pay each month will be the same throughout the years.
- Principal equal payment (元本均等返済): repayment method with a fixed principal amount per repayment added with interest on the principal balance. The total payment each month will be larger in the beginning, as you will have more balance thus more interest payment, and less in the future.
- Bonus repayment (ボーナス併用払い): make a monthly repayment regularly and pay an extra repayment at bonus time
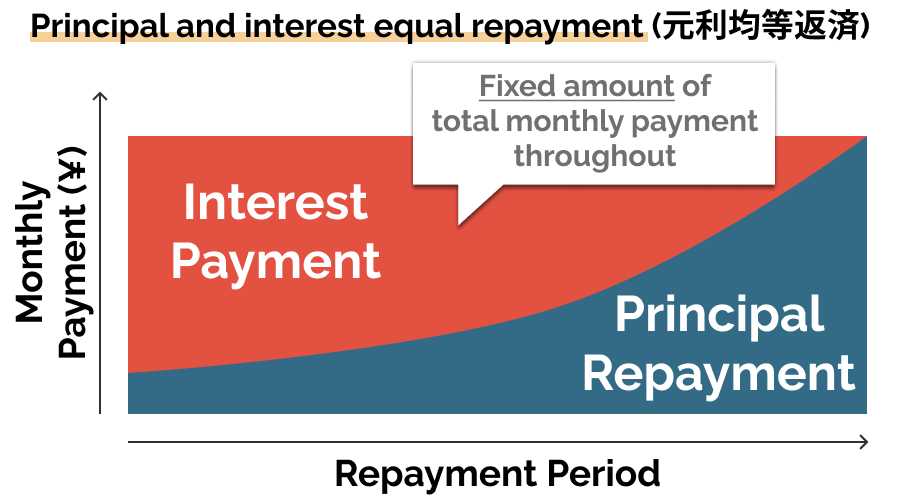
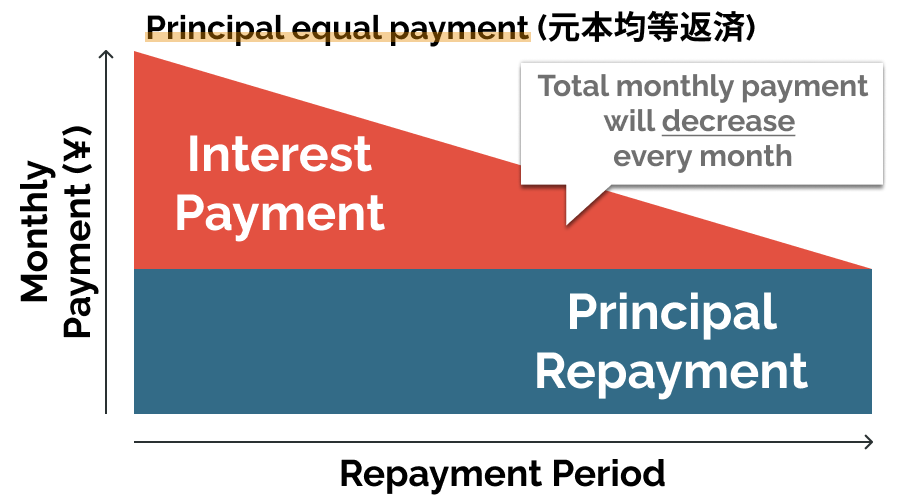
While it is technically possible to take out a house loan in Japan, some foreign individuals may struggle to obtain a house loan in Japan because of some regulations. In the next few chapters, we will explain the procedure and requirements for foreigners to obtain a house loan in Japan.
2. Can foreigners buy real estate in Japan?
Before getting into the details of mortgages in Japan, we want to clarify that all foreigners are permitted to buy land or property in Japan and be the absolute owner of it.

Foreigners can purchase homes and own land for any kind of purpose, and the tax you have to pay for land purchase is the same as the rate paid by any Japanese citizen. Depending on your specific circumstances, it may be a good idea to build or buy your own house in Japan rather than rent.
If you are interested in buying land or property, please also refer to the step-by-step guide to a general house building process in Japan
See also: How to find land for sale in Japan - Find the best property with skilled Japanese architects
3. Can foreigners apply for a house loan in Japan?
The short answer is, yes! Foreigners are eligible for house loans but you have to meet certain criteria to apply for a home loan. Here are some typical requirements which Japanese financial institutions will expect from the applicant:
- Person who is between the ages of 20 and 65, and who will be no older than age 80 when the loan will be fully repaid.
- Person who has a stable income for at least one year as a full-time employee or at least two years as a self-employed or contract worker.
( * working period and the amount of income may vary depending on the financial institution you will choose.) - Person who can get a group credit life insurance.
In addition to the above, the most important criteria for foreign nationals to get a home loan is whether or not you have a permanent residency. Please read the following section for different house loans based on the status of your permanent residency.
4. Do you have a permanent residency?
The reality is that most financial institutions will not consider you a valid applicant for a regular home loan if you do not have a permanent residency in Japan.
However, in recent years, obtaining home loans have become more flexible so that people without a permanent residency can apply for house loans in Japan. In those cases, you might go through an extra detailed check and process of each individual’s situation.
The process and the requirements will be different whether if you have a permanent residency or not:

4-1. Applying a house loan with permanent residency
If you have a permanent resident status, you can take out a house loan just like any other Japanese citizen.
Major requirements to take out a loan will include:
- Annual household income
- Length of employment and employment status in the case of company employees
- Existence and repayment status of other loans.
- (Some banks require you to read and speak Japanese on a certain level.)
4-2. Applying a house loan without permanent residency
At most Japanese financial institutions, home loans are only available to those with permanent residency. In some circumstances, non-permanent residents are also eligible for housing loans. Here are some examples:
Case 1 -- Ask your Japanese spouse to be your guarantor
If the applicant’s spouse is a Japanese citizen or a permanent resident of Japanhe/she can be the joint guarantor for them to apply for the house loan with the bank.
Case 2 -- Using the local branch of a bank from your home country
The applicant might get a house loan by using a bank from your home country. If a bank in your home country has a branch in Japan, you may be able to get a house loan. However, please be careful that the repayment may become difficult if interest rates rise due to sudden changes in the economic situation in your home country.
Case 3 -- Using a bank from your home country
Some international banks will let you take out a house loan in their own currency for purchasing a property in foreign countries, including Japan. You can then convert the funds to Japanese Yen to pay for the property to acquire in japan.
However, it is often more difficult to take this option as the bank in your home country tend not to like lending money for properties outside of their operating regions and have limited access to the collateral.
Case 4 -- Apply for specific house loans for foreigners with additional criteria from a Japanese financial institution
The criteria for applying for a mortgage without a permanent residence differ depending on the financial institution. The general screening points are as follows:
(1) Possibility of becoming a permanent resident in the future
If you have lived in Japan for more than 5 years, the bank could take the fact into account favourably as a sign of possible permanent residency in the future. Although it depends on each financial institution, confirmation of your permanent residence in Japan and its possibility is still a key point in the bank's screening process.
(2) Number of years of work
Applicants are generally required to work for more than 1~3 years with the same company in Japan. The longer your employment status is, the better sign for banks to expect a stable income in Japan.
(3) Ability to pay for down payment
You will usually be asked for 20% or up to 30~50% of the price of your property for down payment in most of the non-permanent resident loans.
In order for applicants to obtain a house loan approval without permanent residence, it is recommended to have as much cash deposit as possible before you purchase a property.
(4) Position of employment
It is easier to apply as a regular employee rather than a business owner. For business owners other than company employees, the screening process might become more difficult to obtain a long-term mortgage loan of more than 10 years due to the lack of retirement benefits and the continuity and stability of the business
In addition, financial institutions tend to look strictly at the stability of the company's performance.
(5) Language
It is advantageous if the applicant is able to write Japanese, understand the contact details, and have a certain level of daily conversation capability. Depending on the bank, a brief interview is mandatory between the applicant and bank representative.
Here are some banks that may consider mortgage applicants without a Permanent Residence status. You can contact the respective banks and ask if you are eligible.
SMBC Trust Bank PRESTIA (formerly Citibank Japan)
https://www.smbctb.co.jp/en/product/loan/housing/
Aeon Bank
https://www.aeonbank.co.jp/housing_loan/
Suruga Bank
https://www.surugabank.co.jp/surugabank/kojin/service/dream_j/
Tokyo Star Bank
https://www.tokyostarbank.co.jp/products/loan/homeloan/homeloan_star/
5. What are the procedures for taking out a housing loan to build a house in Japan?
Here we provide a general example of the process required when applying for a housing loan at a local bank:
- (1) Apply for a housing loan and submit necessary documents to the financial institution
- (2) First review conducted by the institution employee (仮審査)
- (3) Final review conducted by the institution (本審査)
- (4) Signing a loan agreement, establishment of a house loan
- (5) Loan granted your repayment period will start
Learn more from the next article: Housing payments: When, to whom, and how much you need to Pay
As mentioned in the previous chapters, there are various types of house loans provided by different financial institutions in Japan. Also, in order to successfully take over a house loan in Japan, there are various prerequisites that have to be met for foreigners and procedures differ depending on whether you have permanent residence or not.
See also:
6. Summary
Here is the summary to recap this article:
- All foreigners can buy land or a property and most of foreign residents can apply for housing loans in Japan.
- It is preferable to have a permanent residence if you are applying for a house loan to a Japanese financial institution.
- Some financial institutions have house loan products specifically for people without permanent residence
With increasing number of foreigners living in Japan, there are more and more cases of non-Japanese nationals purchasing land and applying for house loans in Japan. With no restrictions or extra tax on foreigners purchasing Japanese property, would you also like to consider having a house custom built in Japan?



